Overview of Emerging Technologies in Healthcare
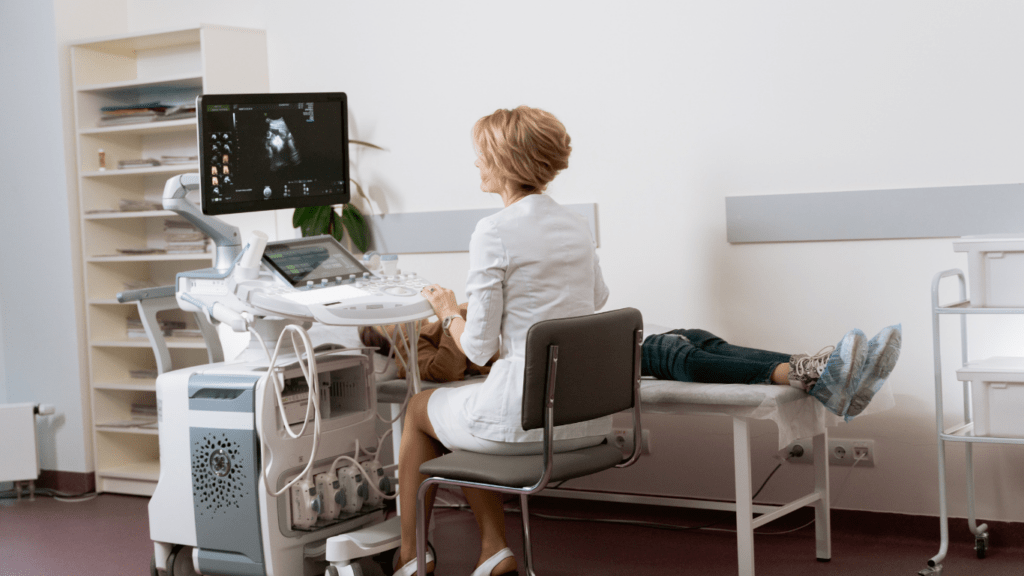
Emerging technologies are redefining healthcare delivery and operations. Innovations like artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming the diagnostic landscape.
AI algorithms analyze complex medical data rapidly, aiding doctors in diagnosing diseases more accurately. For instance, AI models detect early signs of diseases in medical imaging.
Wearable devices are revolutionizing patient monitoring. These gadgets, including smartwatches and fitness trackers, provide real-time health data.
They monitor vital signs like heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity. This continuous data stream enables personalized care and proactive health management.
Telemedicine platforms are enhancing healthcare accessibility.
Patients consult doctors remotely using telehealth services.
For example:
- Video calls
- Online chats
- Mobile apps connect patients and healthcare providers instantly
This reduces the need for in-person visits, particularly beneficial for those in remote or underserved areas.
Blockchain technology ensures secure and transparent health records. It creates immutable patient data ledgers that enhance data security.
This technology reduces fraud and ensures that patient records remain confidential and tamper-proof. Hospitals and clinics are increasingly adopting blockchain for medical records management.
3D printing technology is making significant strides in healthcare. Custom prosthetics and implants are created using 3D printers, tailored to individual patient needs.
This technology enhances precision in surgeries and reduces recovery times by providing perfectly fitting medical devices.
Genomics and personalized medicine are transforming treatment plans. By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, doctors can create customized treatment regimens.
This offers targeted therapies that are more effective and have fewer side effects compared to conventional treatments.
Robotics is revolutionizing surgical procedures. Robotic surgical systems allow for minimally invasive surgeries with high precision.
These systems improve patient outcomes by reducing complication rates and shortening recovery periods.
Robots assist surgeons in performing intricate procedures with enhanced accuracy.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are training tools in medical education.
These technologies create immersive learning experiences for medical students and professionals. VR and AR simulations help in learning complex procedures and anatomy, improving overall medical training efficiency.
By integrating these emerging technologies, healthcare is experiencing unprecedented advancements that foster improved patient outcomes, streamlined operations, and innovative treatment solutions.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning
Diagnosis and Treatment Enhancements
AI and machine learning are transforming diagnostics and treatment plans. These technologies analyze medical data, including:
- Imaging
- Patient records
- To detect patterns that may escape human eyes
For instance, AI can identify breast cancer in mammograms with higher accuracy than human radiologists, according to a study published in Nature (January 2020).
Machine learning algorithms also aid in predicting patient outcomes and recommending personalized treatment regimens, improving the precision of patient care.
Healthcare Workflow Optimization
AI optimizes healthcare workflows by automating tasks and reducing administrative burdens.
Natural language processing (NLP) tools extract critical information from electronic health records (EHRs), streamlining data entry and ensuring accuracy.
For example, AI-powered systems for scheduling and resource allocation enhance operational efficiency by predicting patient appointment no-shows and optimizing staff deployment.
Machine learning models also forecast inventory needs, minimizing shortages and reducing costs. These innovations lead to more efficient healthcare delivery and improved patient experiences.
Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare

Expanding Access to Care
Telemedicine enhances healthcare access, breaking down geographical barriers. Rural areas benefit from virtual consultations, where patients connect with specialists remotely.
With platforms like Teladoc and Amwell, remote monitoring becomes feasible, enabling follow-up care without travel. Chronic disease management improves as doctors monitor conditions such as:
- Diabetes
- Hypertension remotely
- Adding a layer of convenience and timely intervention
Integration With Wearable Tech
Wearable technology complements telemedicine by providing real-time health data.
Devices like Fitbit and Apple Watch track vital signs, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patient health continuously.
These devices send data to telemedicine platforms, where AI algorithms analyze it for anomalies.
Early detection of conditions like atrial fibrillation becomes possible.
Integrating wearables with remote healthcare systems fosters proactive health management, enhancing patient outcomes through continuous monitoring.
Blockchain for Enhanced Privacy and Security
Securing Patient Data
Blockchain technology secures patient data by creating immutable records. Each data block gets linked to the previous one, ensuring no unauthorized alterations can occur without detection.
This feature is crucial for maintaining data integrity in healthcare systems. According to a 2019 study by IBM, over 50% of healthcare executives recognize blockchain’s potential in securing patient data.
Blockchain also helps prevent data breaches, which are a significant concern in healthcare.
For instance, the 2021 Healthcare Data Breach Report recorded 714 data breaches, affecting 45 million individuals. Blockchain encryption can reduce these incidents, fostering trust in digital health solutions.
Streamlining Medical Records
Blockchain streamlines medical records by offering a unified, decentralized database. This eliminates fragmentation, allowing healthcare providers to access up-to-date patient data efficiently.
A 2020 report by Deloitte highlights that 55% of surveyed healthcare organizations believe blockchain can improve medical data management. With this tech, patients control their records, which enhances transparency.
Care coordination among specialists improves through shared access to critical medical history.
For example, an oncologist and a cardiologist can simultaneously review a patient’s treatment history and current medications, making collaborative care seamless.
Together, these applications of blockchain contribute to higher privacy, efficiency, and security in healthcare, enabling a more reliable and streamlined system.
The Role of 3D Printing
Custom Medical Devices and Prosthetics
Custom medical devices and prosthetics directly impact patient care by providing personalized solutions. 3D printing allows for the rapid production of tailor-made medical devices, such as:
- Hearing aids
- Dental implants
- Ensuring precise fit and comfort
This technology significantly reduces the time and cost associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
For instance, producing a custom prosthetic limb through 3D printing can take a few days, as opposed to weeks or months with conventional methods.
This expedited production supports quicker patient recovery and enhances overall patient satisfaction.
Innovations in Bioprinting
Innovations in bioprinting are transforming regenerative medicine by enabling the creation of biological structures. 3D bioprinters can layer living cells to create tissues like skin, cartilage, and even organ prototypes.
Researchers are exploring the potential for 3D-printed organs, which holds the promise of reducing organ transplant wait times.
According to data from the American Transplant Foundation, more than 114,000 people in the U.S. are on the organ transplant waiting list.
Successful bioprinting could drastically change these statistics by offering an alternative to donor organs.

 Alice McClurg - Content Director Alice McClurg leads the editorial team as Content Director at Jackpot Journey Spot. With a keen eye for emerging trends and a deep understanding of the gambling landscape, Alice curates in-depth articles, event highlights, and game overviews. Her expertise helps guide readers through the ever-evolving world of gambling, ensuring they stay informed and entertained.
Alice McClurg - Content Director Alice McClurg leads the editorial team as Content Director at Jackpot Journey Spot. With a keen eye for emerging trends and a deep understanding of the gambling landscape, Alice curates in-depth articles, event highlights, and game overviews. Her expertise helps guide readers through the ever-evolving world of gambling, ensuring they stay informed and entertained.
